[et_pb_section fb_built=”1″ _builder_version=”4.7.0″ custom_margin=”0px||0px||false|false” custom_padding=”0px||0px||false|false”][et_pb_row column_structure=”3_4,1_4″ use_custom_gutter=”on” gutter_width=”1″ _builder_version=”4.7.3″ _module_preset=”default” width=”100%” custom_margin=”0px||||false|false” custom_padding=”3px||5px|||” border_width_bottom=”1px” border_color_bottom=”#a6c942″][et_pb_column type=”3_4″ _builder_version=”4.7.0″ _module_preset=”default”][et_pb_post_title meta=”off” featured_image=”off” _builder_version=”4.7.4″ _module_preset=”default” title_font=”||||||||” custom_margin=”||3px|||” border_color_bottom=”#a6c942″][/et_pb_post_title][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type=”1_4″ _builder_version=”4.7.0″ _module_preset=”default”][et_pb_image src=”https://edmontonsocialplanning.ca/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/boxes_1.gif” title_text=”boxes_1″ align=”center” disabled_on=”on|off|off” _builder_version=”4.7.4″ _module_preset=”default” width=”100%” custom_margin=”-2px||-1px||false|false” custom_padding=”||7px|||”][/et_pb_image][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][et_pb_row column_structure=”3_4,1_4″ use_custom_gutter=”on” gutter_width=”1″ make_equal=”on” _builder_version=”4.7.4″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat” width=”100%” custom_margin=”0px|auto|0px|auto|false|false” custom_padding=”37px|0px|44px|0px|false|false”][et_pb_column type=”3_4″ _builder_version=”4.5.6″ custom_padding=”0px|0px|0px|0px|false|false” custom_padding__hover=”|||”][et_pb_text _builder_version=”4.7.4″ _dynamic_attributes=”content” _module_preset=”default” text_font=”||||||||” text_text_color=”#000000″ custom_padding=”||32px|||”]@ET-DC@eyJkeW5hbWljIjp0cnVlLCJjb250ZW50IjoicG9zdF9kYXRlIiwic2V0dGluZ3MiOnsiYmVmb3JlIjoiIiwiYWZ0ZXIiOiIiLCJkYXRlX2Zvcm1hdCI6ImRlZmF1bHQiLCJjdXN0b21fZGF0ZV9mb3JtYXQiOiIifX0=@[/et_pb_text][et_pb_button button_url=”https://edmontonsocialplanning.ca/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Statement-on-Systemic-Racism-Final.pdf” button_text=”Download the Full Statement on Systemic Racism” _builder_version=”4.7.4″ _module_preset=”default” custom_button=”on” button_text_color=”#ffffff” button_bg_color=”#008ac1″ custom_margin=”||19px|||” custom_padding=”||5px|||” hover_enabled=”0″ sticky_enabled=”0″][/et_pb_button][et_pb_text _builder_version=”4.7.4″ text_line_height=”1.6em” header_2_font=”||||||||” header_2_text_color=”#008ac1″ header_2_font_size=”24px” background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat” width=”95%” module_alignment=”left” custom_margin=”44px|0px|2px|-96px|false|false” hover_enabled=”0″ locked=”off” sticky_enabled=”0″]
The Edmonton Social Planning Council stands in solidarity with the Black and Indigenous communities of Canada to end systemic racism and discrimination. These prejudices are reinforced by systems of power that actively harm Black and Indigenous individuals, families, and communities. These inequalities are unjust and the policies, practices, and attitudes that lead to discrimination must be dismantled.
Long have we known that racism contributes directly to economic harm here in Canada. Recent data has shown that racialized individuals are more than twice as likely to be in poverty compared to their non-racialized counterparts (Figure 1), and almost one in five Black Edmontonians are low-income, compared to less than one in ten non-Visible Minority. Racialized workers are also more likely to be unemployed (9.2% vs 7.3% as of 2016). This is despite the fact that racialized workers are more active in the labour force, either working or trying to find work. Since 2006, this trend has only gotten worse.
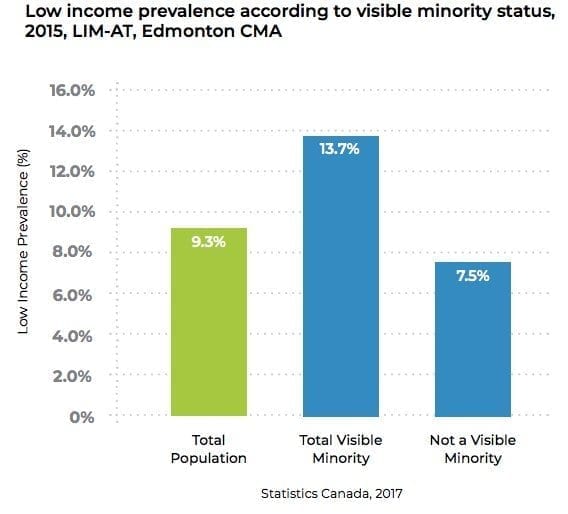
Another way of highlighting the impacts of racism and employment is to break down the effects of income disparity between different racialized groups. Black and Indigenous communities are still the most likely to be in poverty. People are treated differently based on their skin colour, including tenants who are rejected by their landlords, applicants who are turned away from prospective employers, and those looking for acceptance in community programs. These glaring disparities result in unacceptable gaps in health outcomes, educational attainment, and mental health challenges among racialized groups. We must work diligently to close these gaps so that our communities thrive in an equitable and just manner. See our list of past publications at the bottom for more data on these inequalities.
It is a myth that racism has been eradicated in Canada. There are many ways to get involved and begin to change this:
- Sign petitions denouncing racist policies and actions here in Canada.
- Engage with your local city councillor, school board trustee, MLA, and MP and ask them how they plan to incorporate an anti-racist framework in their policies and legislation.
- Speak out against micro-aggressions that you may see in your day-to-day life.
- Read written works by Black and Indigenous authors in Canada: Desmond Cole, Rinaldo Walcott, Sheila Watt-Cloutier, Jesse Thistle, and many more.
- Donate to one of the various Black, Indigenous, BIPOC-led organizations in Edmonton and Canada.
Local (YEG) BIPOC Organizations you can support:
- 5 Artists 1 Love (https://www.5artists1love.com/)
- Africa Centre (https://www.africacentre.ca/)
- APIRG (https://apirg.org/)
- BIPOC in Bloom (https://www.instagram.com/bipocinbloom/)
- Black Arts Matter YEG (https://www.facebook.com/BAMyeg/)
- Black Lives Matter YEG (https://www.blmyeg.com/)
- Black Women United YEG (https://www.bwunited.ca/)
- Black Youth Helpline (https://blackyouth.ca/)
- Council for Canadians of African and Caribbean Heritage (http://ccach.org/)
- Edmonton 2 Spirit Society (http://e2s.ca/)
- Edmonton Centre for Race and Culture (https://cfrac.com/)
- iHuman Youth Society (https://ihuman.org/)
- La Connexion Afro Latina (https://www.laconnexional.com/)
- Multicultural Family Resources Society (https://mfrsedmonton.org/)
- Multicultural Health Brokers (http://mchb.org/)
- National Black Coalition of Canada Society – Edmonton Chapter (http://www.nbccedmonton.ca/)
- Raricanow (https://raricanow.org/)
- Shades of Colour (https://www.patreon.com/shadesofcolour)
- The Canadian Native Friendship Centre YEG (http://www.cnfc.ca/)
- The Come Up (https://www.yegthecomeup.com/)
Sources:
Edmonton Community Foundation and Edmonton Social Planning Council. (2015). Vital Signs: Edmonton’s Urban Aboriginal Population. https://edmontonsocialplanning.ca/vital-signs-edmonton-2015-2/
Edmonton Community Foundation and Edmonton Social Planning Council. (2016). Vital Signs: Immigrants. https://edmontonsocialplanning.ca/vitalsigns-2016/
Edmonton Community Foundation and Edmonton Social Planning Council. (2019). Vital Topic: Indigenous Women in Alberta. https://edmontonsocialplanning.ca/vital-topic-indigenous-women-in-alberta/
Ngo, S. and Kolkman, J. (2019). A Profile of Poverty in Edmonton. Updated May 2019. Edmonton Social Planning Council. https://edmontonsocialplanning.ca/a-profile-of-poverty-in-edmonton-may-2019-update-2/
Block, S., Galabuzi, G., and Tranjan, R. (2019). Canada’s Colour Coded Income Inequality. Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives.
https://www.policyalternatives.ca/publications/reports/canadas-colour-coded-income-inequality
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type=”1_4″ _builder_version=”4.7.4″ custom_padding=”0px|20px|0px|20px|false|false” border_color_left=”#a6c942″ custom_padding__hover=”|||”][et_pb_testimonial author=”Posted by:” job_title=”@ET-DC@eyJkeW5hbWljIjp0cnVlLCJjb250ZW50IjoicG9zdF9hdXRob3IiLCJzZXR0aW5ncyI6eyJiZWZvcmUiOiIiLCJhZnRlciI6IiIsIm5hbWVfZm9ybWF0IjoiZGlzcGxheV9uYW1lIiwibGluayI6Im9uIiwibGlua19kZXN0aW5hdGlvbiI6ImF1dGhvcl93ZWJzaXRlIn19@” portrait_url=”@ET-DC@eyJkeW5hbWljIjp0cnVlLCJjb250ZW50IjoicG9zdF9hdXRob3JfcHJvZmlsZV9waWN0dXJlIiwic2V0dGluZ3MiOnt9fQ==@” quote_icon=”off” disabled_on=”on|off|off” _builder_version=”4.7.4″ _dynamic_attributes=”job_title,portrait_url” _module_preset=”default” body_text_color=”#000000″ author_font=”||||||||” author_text_align=”center” author_text_color=”#008ac1″ position_font=”||||||||” position_text_color=”#000000″ company_text_color=”#000000″ background_color=”#ffffff” text_orientation=”center” module_alignment=”center” custom_margin=”0px|0px|4px|0px|false|false” custom_padding=”32px|0px|0px|0px|false|false”][/et_pb_testimonial][et_pb_text disabled_on=”on|off|off” _builder_version=”4.7.4″ _dynamic_attributes=”content” _module_preset=”default” text_text_color=”#000000″ header_text_align=”left” header_text_color=”rgba(0,0,0,0.65)” header_font_size=”20px” text_orientation=”center” custom_margin=”||50px|||” custom_padding=”48px|||||”]@ET-DC@eyJkeW5hbWljIjp0cnVlLCJjb250ZW50IjoicG9zdF9jYXRlZ29yaWVzIiwic2V0dGluZ3MiOnsiYmVmb3JlIjoiUmVsYXRlZCBjYXRlZ29yaWVzOiAgIiwiYWZ0ZXIiOiIiLCJsaW5rX3RvX3Rlcm1fcGFnZSI6Im9uIiwic2VwYXJhdG9yIjoiIHwgIiwiY2F0ZWdvcnlfdHlwZSI6ImNhdGVnb3J5In19@[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]

